|
There are several ways that the route instructions could be specified on
a Pegularity: 1.0 Descriptive Instructions
The route instructions could be purely descriptive like this example
From the front gate, cross the road and enter the footpath. Continue
until you reach the road junction and turn right. Take the first
footpath left after 0.223 miles. Continue to the tarmac road and turn
right. Take the next road left. After 0.19 miles turn left onto the
footpath. Continue to the tarmac road, turn right. Turn left onto the
footpath leading to Renters Farm. At the farm turn left onto the road
and continue for about 1 mile back to where you started.
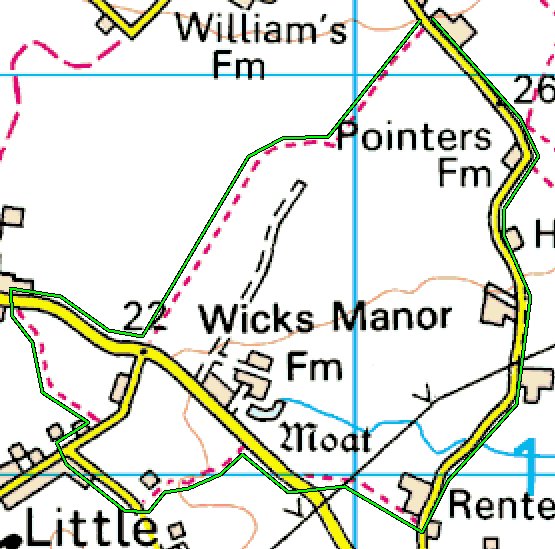
2.0 Marked Map
You might be given a marked section of a map, like the Ordnance
Survey example below.
The accompanying instructions might read:
From the front gate, cross the road and enter the footpath. Follow the
route denoted by the green line and return to the front gate.
3.0 Basic Map
You might be given the the same map section, but without the green
line. Here are some forms that you might encounter to describe the route.
3.1 Basic Map - Descriptive Instructions
The description could be similar to that in paragraph 1.0 above.
3.2 Basic Map - Simple Directions only
The route might be defined by simple directions without distances:
From the front gate, cross the road and enter the footpath. Continue
to the end and turn right. Take the first footpath left. Continue to the
tarmac road and turn right. Take the next road left. Turn left onto the
footpath. Continue to the tarmac road, turn right. Turn left onto the
footpath. At the end turn left and continue to return to where you
started.
3.3 Basic Map - Using map detail
Navigation might be by reference to map features. For example
Cross the road and enter the footpath. Turn west at spot height 22.
Use three footpaths then go under an electricity transmission line.
Continue by the shortest route to return to where you started.
3.4 Basic Map - Cryptic Instructions
Anything goes here. For example, you might have to solve a puzzle
like this:
Red: 23, 8, 6, 7 then home.
This cryptic clue actually refers to the red dashes that are used to
define a footpath. There are 23 dashes on the footpath opposite the
start, and 8, 6 and 7 on the other footpaths that are to be used.
Organiser's Maps
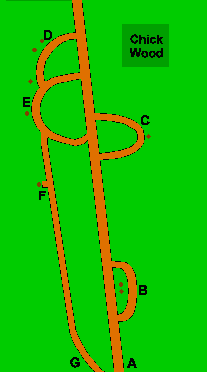 Instead of
using sections of Ordnance Survey maps, the organisers may provide their
own maps particularly if the route uses, say, private land or public
parks. Instead of
using sections of Ordnance Survey maps, the organisers may provide their
own maps particularly if the route uses, say, private land or public
parks.
Here's an example through Chick Wood.
The route instructions might say:
Start at A, then go via B, C, D, E, F and finish at G
Speed Changes
The route instructions might include additional requirements like:
The third footpath is quite bumpy and overgrown - Reduce your nominated
average speed (NAS) by 20%.
This means that if your NAS for the Pegularity was, say, 3 mph, then
while following the third footpath, you should reduce your
average speed to 2.4 mph. The target time for you will have taken this
into account, so you will have to adjust your walking speed accordingly.
Route Checks
To check that you have followed the correct Pegularity route, the
route instructions may pose some Route Checks for you to answer. You'll
need to write your answers on the Pegularity Sheet you were given at the
start of the Pegularity.
For example, using the Ordnance Survey map above, you might see:
Route Check 1: Name of the house on the third footpath?
Route Check 2: 0.534 miles after you go under the electricity
transmission line, how many ducks on the sign?
Or using the organiser's map above, you might see:
Route Check 1: Write down the 3-letter code on the tree at point B.
Route Check 2: Number on the gate between points D and E?
|


 Instead of
using sections of Ordnance Survey maps, the organisers may provide their
own maps particularly if the route uses, say, private land or public
parks.
Instead of
using sections of Ordnance Survey maps, the organisers may provide their
own maps particularly if the route uses, say, private land or public
parks.